EN420:2003
EN420 is the general requirements for most protective gloves to ensure that the gloves themselves do not cause any harm to wearer and are comfortable to wear. Tests included in this standard are: sizing, dexterity, pH value, and chrome VI.
The EN388 sets standards for five types of protection: abrasion resistance, cut resistance, tear resistance, puncture resistance, and impact protection through 6 tests:
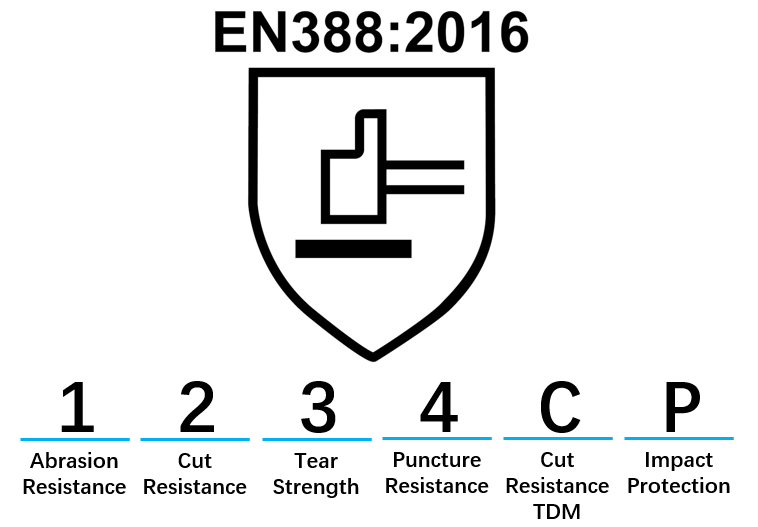
Type |
Level |
Equipment |
Measurement |
|
Abrasion Resistance Test |
1-4 |
 |
Abrasion until a hole appears on the material |
|
Cut Resistance, Coup Test |
1-5 |
 |
Knife pass over the material until cut through |
|
Tearing Strength Test |
1-4 |
 |
Tear until the material is apart |
|
Puncture Resistance Test |
1-4 |
 |
Puncture the material until a tip appears |
|
Cut Resistance, TDM TEST ISO 13997 |
A-F |
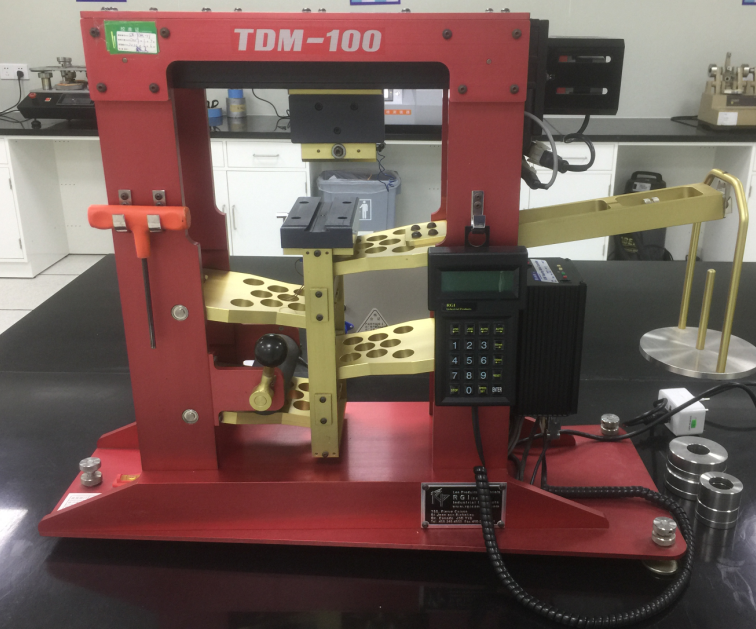 |
Add force until cut through at 20mm length |
|
Impact Protection Test |
P/NP |
|
|
TDM test is given when the material dulls the knife during Coup test.
EN511 sets standards for low temperature protection gloves.
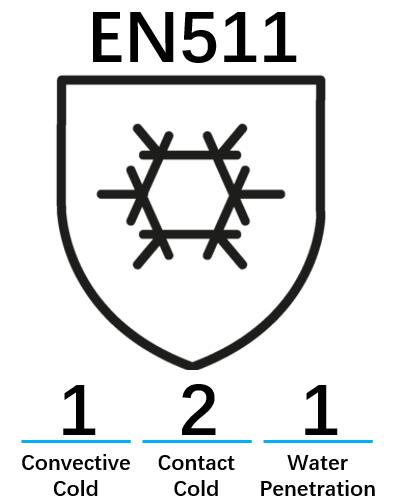
The first figure shows the level of protection against convective cold from 0-4.
The second figure shows the level of protection against contact cold from 0-4.
The third figure shows whether the glove is water penetration after 30 minutes. 1 stands for no water penetration after 30 minutes.

EN407 is the heat protection standard for protective gloves. 6 numbers stand for 6 types of heat hazard protection level.
Type |
Level |
Measurement |
|
Flammability |
0-4 |
Material damage after burning |
|
Contact heat |
0-4 |
The rate of temperature rise while contacting with a hot probe |
|
Convective heat |
0-4 |
The rate of temperature rise while contacting with a gas flame |
|
Radiant heat |
0-4 |
The rate of temperature rise while contacting with radiant heat |
|
Small drops of molten metal |
0-4 |
The rate of temperature rise while contacting small drops of molten metal |
|
Large drops of molten metal |
0-4 |
Grams of molten iron needed to damage the PVC film on the back of the glove material. |
EN374 gives directives of how to test permeation and degradation by the 18 chemicals that would lead to cracking or holing.
Three specimens are taken from the palm (another three specimens are also taken from the cuff if gloves are longer than 400mm and claimed to provide protection) to test in the following 18 chemical, but not the mixture of any two.
|
Code letter |
Chemical |
CAS No. |
Class |
|
A |
Methanol |
67-56-1 |
Primary alcohol |
|
B |
Acetone |
67-64-1 |
Ketone |
|
C |
Acetonitrile |
1975/5/8 |
Nitrile compound |
|
D |
Dichloromethane |
1975/9/2 |
Chlorinated paraffin |
|
E |
Carbon disulphide |
75-15-0 |
Organic compound containing sulphur |
|
F |
Toluene |
108-88-3 |
Aromatic hydrocarbon |
|
G |
Diethylamine |
109-89-7 |
Amine |
|
H |
Tetrahydrofuran |
109-99-9 |
Heterocyclic and ether compound |
|
I |
Ethyl acetate |
141-78-6 |
Ester |
|
J |
n-heptane |
142-82-5 |
Saturated hydrocarbon |
|
K |
40% Sodium hydroxide |
1310-73-2 |
Inorganic base |
|
L |
96% Sulphuric acid |
7664-93-9 |
Inorganic mineral acid |
|
M |
65% nitric acid |
7697-37-2 |
Inorganic mineral acid |
|
N |
99% acetic acid |
64-19-7 |
Organic acid |
|
O |
25% ammonium hydroxide |
1336-21-6 |
Organic base |
|
P |
30% hydrogen peroxide |
7722-84-1 |
Peroxide |
|
S |
40% hydrofluoric acid |
7664-39-3 |
Inorganic mineral acid |
|
T |
37% formaldehyde |
50-00-0 |
Aldehyde |
Type A gloves have a breakthrough time of 30min or more against minimum 6 test chemicals.
Type B gloves have a breakthrough time of 30min or more against minimum 3 test chemicals.
Type C gloves have a breakthrough time of 10min or more against minimum 1 test chemical.
OEKO - Tex® Standard 100
OEKO - Tex® Standard 100 is a textile tested standard for harmful substances. Testing subjects include prohibited azo dyes, formaldehyde, nickel, chemicals harmful to health, etc. Around 100 test parameters are taken into account. For more information, please vist https://www.oeko-tex.com/en/our-standards/standard-100-by-oeko-tex